15 分钟 阅读
SpringBoot + Gradle学习记录
简化的Spring配置
介绍
通过Spring Boot可以轻松地创建和运行独立的,可以商用的应用程序
优点:
- 可以创建独立的Spring程序
- 直接嵌入Tomcat, Jetty或者Undertow等容器(无需部署WAR文件)
- 提供一些默认依赖项,简化构建配置,尽可能自动配置Spring和三方库,让开发者更快入门
- 没有冗余代码生成和XML配置的要求
我们将介绍一些核心配置、前端、快速数据操作和异常处理。
创建基础项目
先来创建一个Spring Boot的工程,我们可以用如下几种方式:
方式1.用官网的初始化工具
使用官方提供的在线初始化工具 spring initializr
我们选择 Kotlin 语言, 选择 Gradle
用Kotlin时,Gradle是最常用的构建工具,它提供了Kotlin的DSL。
填写项目的基本信息。 然后选择依赖的库:
- Spring Web:用来构建Web应用(包括Restful)
- Spring Security:针对Spring应用程序的高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架。
- Lombok:帮助减少样板代码的Java注释库
- Spring Data JPA:在JPA规范下提供Repository层的实现,可以很方便的切换ORM框架。
- H2 Database:一个开源的嵌入式数据库引擎。
- Thymeleaf:一个用于web和独立环境的现代服务器端的Java模板引擎。允许在静态浏览器中正确显示
依次选上web,security,lombok,jpa,h2,thymeleaf等依赖库
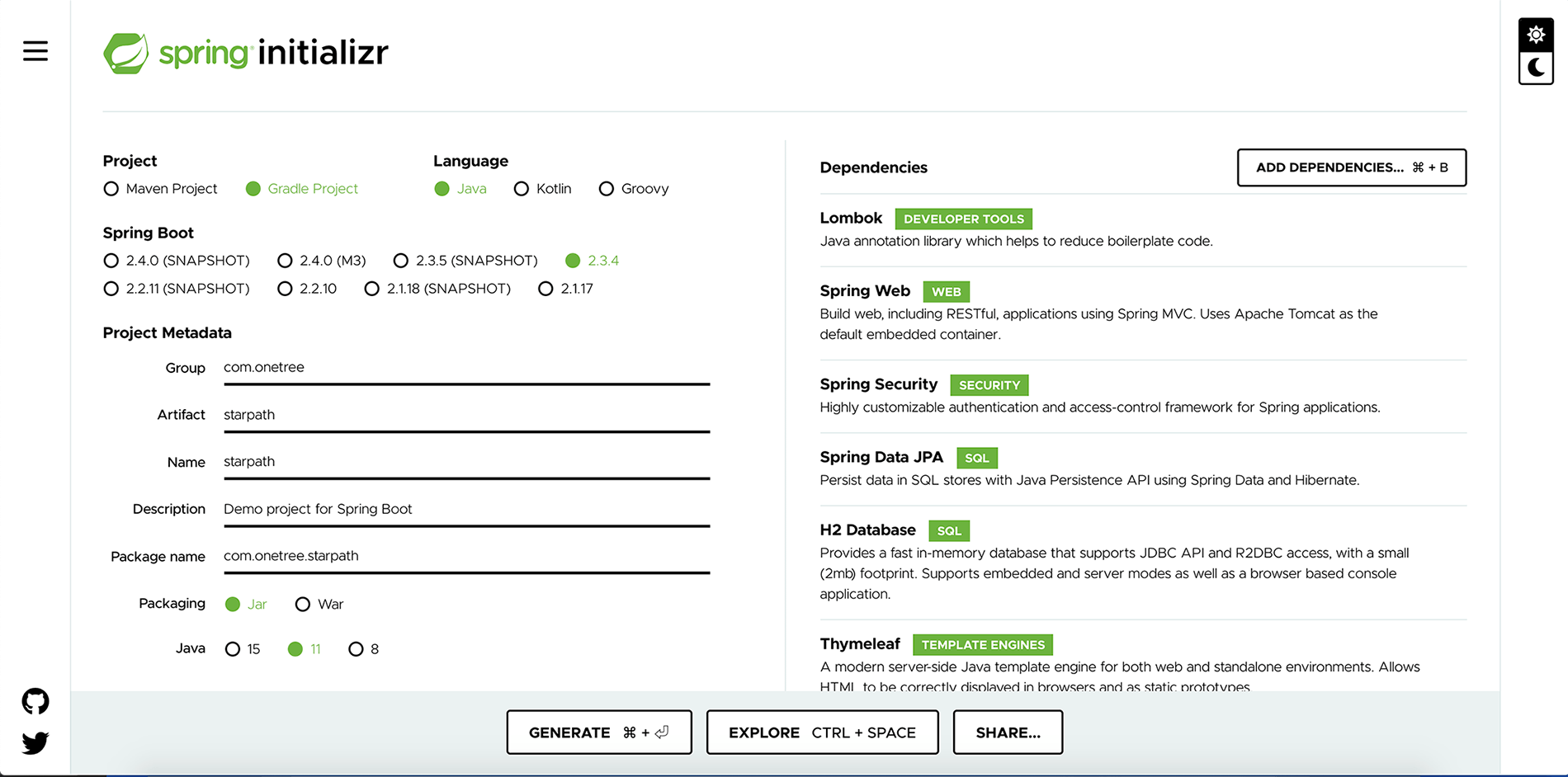
- 点击 GENERATE 会下载一个压缩包,名字和Artifact利配置的一样
- 解压下载下来的starpath.zip, 并用编译器以Gradle方式导入(比如IntelliJ IDEA): Import Project(或者File -> Open) -> Import project from external model -> Gradle,然后一路Next。
方式2.用命令行
在终端里输使用 Initializr HTTP API
$ mkdir starpath && cd starpath
$ curl https://start.spring.io/starter.zip -d language=java -d style=web,security,lombok,jpa,h2,thymeleaf -d packageName=com.onetree.starpath -d name=StarPath -o starpath.zip -d type=gradle-project
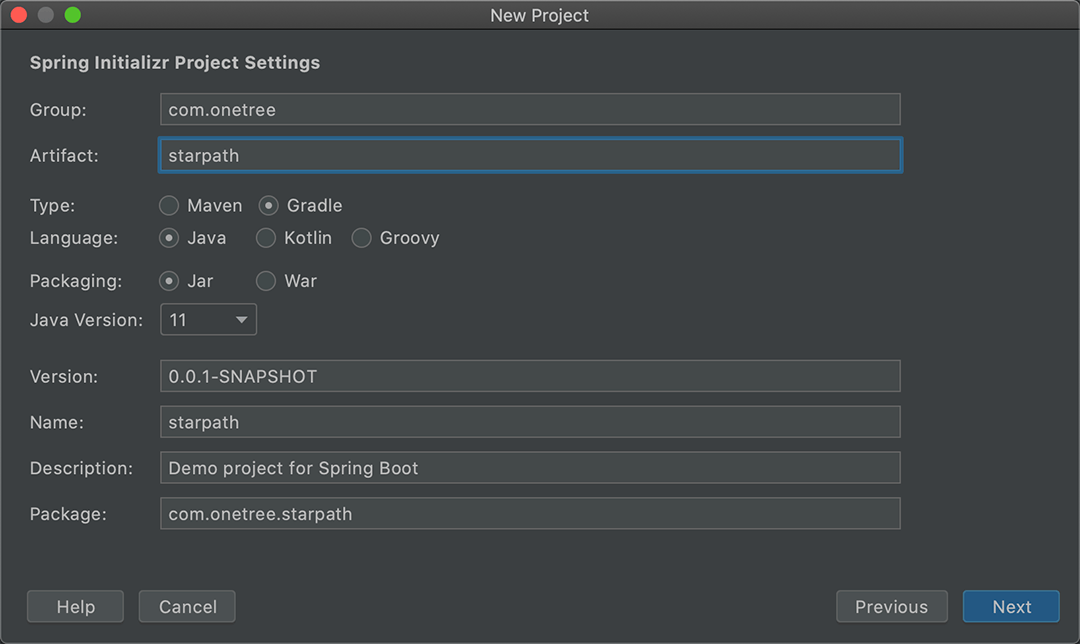
方式3.使用IntelliJ IDEA
如果使用的额是UntelliJ IDEA, 可以在IDE中直接创建Spring Boot的项目:
File -> New -> Spring Initializr, 后面配置跟官网差不多,
 Dependencies选择 Developer Tools -> 依次选上web,security,lombok,jpa,h2,thymeleaf等依赖库
Dependencies选择 Developer Tools -> 依次选上web,security,lombok,jpa,h2,thymeleaf等依赖库
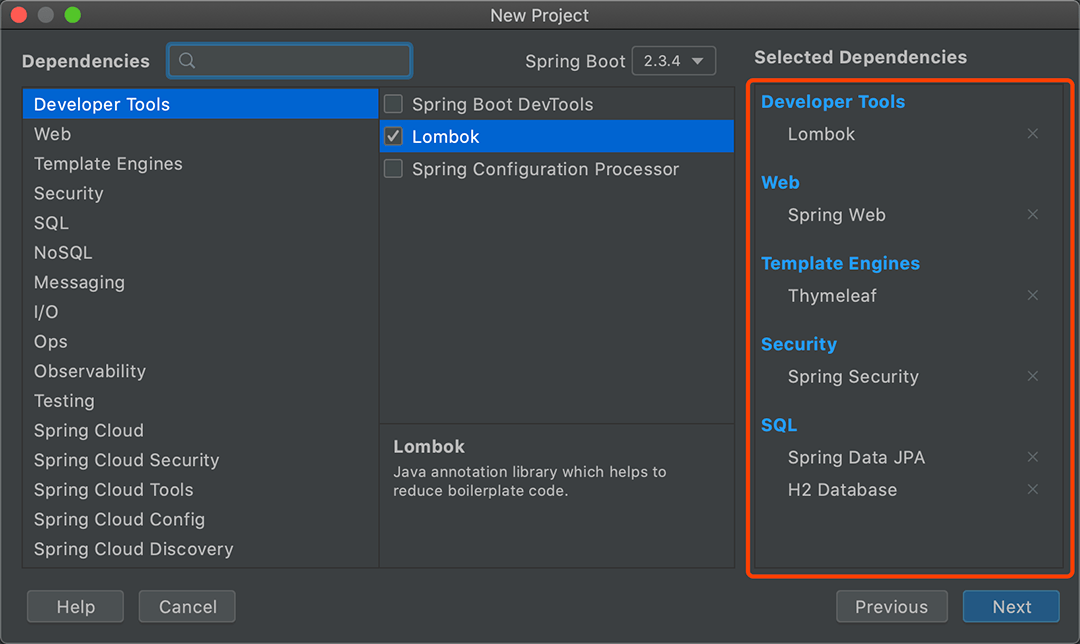 点击Next,配置工程目录,Finish就完成项目的创建了。
点击Next,配置工程目录,Finish就完成项目的创建了。
Gradle
根据上面流程创建完基础项目以后,build.gradle是这样的:
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.3.4.RELEASE'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.0.10.RELEASE'
id 'java'
}
group = 'com.onetree'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = '11'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
runtimeOnly 'com.h2database:h2'
// 一款java代码生成器
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.14'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.14'
// test ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
testImplementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test') {
exclude group: 'org.junit.vintage', module: 'junit-vintage-engine'
}
testImplementation 'org.springframework.security:spring-security-test'
// 一款java代码生成器 for test
testCompileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.14'
testAnnotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.14'
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
application配置
接下来,我们可以为我们的应用程序配置一个简单的主类,看下 {package}/StarpathApplication.java
package com.onetree.starpath;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class StarpathApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StarpathApplication.class, args);
}
}
注意:我们是如何使用
@SpringBootApplication作为我们的主要应用程序配置类的 它相当于@Configuration,@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan的共同作用。
我们可以在 application.properties 里对应用程序配置, 比如将默认端口号8080指定为其他端口号:
server.port=8081
更多的配置可以参考 可用的 Spring Boot properties
简单的MVC视图
现在让我们使用Thymeleaf添加一个简单的前端。
默认情况下启用Thymeleaf不需要额外的配置。
现在我们在 resources/application.properties 进行配置:
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
spring.thymeleaf.enabled=true
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
spring.application.name=Bootstrap Spring Boot
下一步,我们将定义一个简单的Controller(控制器)和一个基本主页,并显示一条欢迎消息,看下 {package}/controller/SimpleController.java
package com.onetree.starpath.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller
public class SimpleController {
@Value("${spring.application.name}")
String appName;
@GetMapping("/")
public String homePage(Model model) {
model.addAllAttributes(Map.of("appName", appName));
return "home";
}
}
最后,这是我们的 resources/templates/home.html
<html xmlns:th="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" lang="en">
<head><title>Home Page</title></head>
<body>
<h1>Hello !</h1>
<p>Welcome to <span th:text="${appName}">Our App</span></p>
</body>
</html>
请注意我们是如何使用在 application.properties 中定义的属性,然后在 SimpleController 注入该属性,以便在主页上显示它。
Security
一旦 spring-boot-starter-security 依赖于应用程序的类路径,那么默认情况下所有端点都是安全的,使用 httpBasic 或基于 Spring Security 内容协商策略的formLogin。
这就是为什么,如果在类路径上有starter,我们通常应该通过扩展 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 类来定义我们自己的自定义安全配置:看下 {package}/config/SecurityConfig.java
package com.onetree.starpath.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest()
.permitAll()
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}
在我们的示例中,我们允许不受限制地访问所有端点。
当然, Spring Security有丰富的功能,不是几行代码就能说得清楚的,想了解更多请参考 Security with Spring
简单的持久化
首先定义我们的数据模型 —— 一个简单的 Book实体:
看下 {package}/persistence/model/Book.java
package com.onetree.starpath.persistence.model;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Entity
public class Book {
@Id
private long id;
private String title;
private String author;
}
以及它的repository(存储库),充分利用了这里的Spring数据:
看下 {package}/persistence/repo/BookRepository.java
package com.onetree.starpath.persistence.repo;
import com.onetree.starpath.persistence.model.Book;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import java.util.List;
public interface BookRepository extends CrudRepository<Book, Long> {
List<Book> findByTitle(String title);
}
最后,我们当然需要配置新的持久层:
...
+++++++++++++++++ start
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
@EnableJpaRepositories("com.onetree.starpath.persistence.repo")
@EntityScan("com.onetree.starpath.persistence.model")
+++++++++++++++++ end
@SpringBootApplication
public class StarpathApplication {
...
}
请注意,我们使用的是:
@EnableJpaRepositories能够扫描指定包中的存储库@EntityScan来获取我们的JPA实体
为了简单起见,我们在这里使用了一个H2内存数据库,这样我们在运行项目时就没有任何外部依赖性。
一旦我们包含H2依赖项,SpringBoot自动检测它并设置持久性,除了数据源属性之外,不需要额外配置.
现在我们在 resources/application.properties 进行数据源属性配置:
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:bootapp;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
当然,与安全性一样,关于持久性想深入了解请看:Spring Persistence Tutorial
Web和Controller
接下来,让我们看一看web层,我们将从设置一个简单的控制器BookController开始。
我们将通过一些简单的验证来实现基本的CRUD操作来公开图书资源:看下 {package}/controller/BookController.java
package com.onetree.starpath.controller;
import com.onetree.starpath.exception.BookIdMismatchException;
import com.onetree.starpath.exception.BookNotFoundException;
import com.onetree.starpath.persistence.repo.BookRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import com.onetree.starpath.persistence.model.Book;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
@GetMapping
public Iterable findAll() {
return bookRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/title/{bookTitle}")
public List findByTitle(@PathVariable String bookTitle) {
return bookRepository.findByTitle(bookTitle);
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Book findOne(@PathVariable Long id) {
return bookRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(BookNotFoundException::new);
}
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public Book create(@RequestBody Book book) {
return bookRepository.save(book);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void delete(@PathVariable Long id) {
bookRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(BookNotFoundException::new);
bookRepository.deleteById(id);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public Book updateBook(@RequestBody Book book, @PathVariable Long id) {
if (book.getId() != id) {
throw new BookIdMismatchException();
}
bookRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(BookNotFoundException::new);
return bookRepository.save(book);
}
}
考虑到这是一个API,我们在这里使用了 @RestController 注释(它相当于 @Controller 和 @ResponseBody),以便每个方法将返回的资源作为HTTP响应数据。
只需指出一点:我们将Book实体作为外部资源公开。对于我们这里的简单应用程序来说,这没问题,但在实际应用程序中,您可能需要将这两个概念分开。参考:Entity To DTO Conversion for a Spring REST API
Error处理
现在核心应用程序已经准备好了,让我们看看如何使用 @ControllerAdvice 来简单的做集中错误处理:看下 {package}/exception/RestExceptionHandler.java
package com.onetree.starpath.exception;
import org.hibernate.exception.ConstraintViolationException;
import org.springframework.dao.DataIntegrityViolationException;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler({ BookNotFoundException.class })
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleNotFound(
Exception ex, WebRequest request) {
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, "Book not found",
new HttpHeaders(), HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, request);
}
@ExceptionHandler({ BookIdMismatchException.class,
ConstraintViolationException.class,
DataIntegrityViolationException.class })
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleBadRequest(
Exception ex, WebRequest request) {
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, ex.getLocalizedMessage(),
new HttpHeaders(), HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST, request);
}
}
除了我们在这里处理的标准异常之外,我们还使用了2个自定义异常,分别是
{package}/exception/BookNotFoundException.java
package com.onetree.starpath.exception;
public class BookNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
public BookNotFoundException() {
super();
}
public BookNotFoundException(final String message, final Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public BookNotFoundException(final String message) {
super(message);
}
public BookNotFoundException(final Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
以及{package}/exception/BookIdMismatchException.java
package com.onetree.starpath.exception;
public class BookIdMismatchException extends RuntimeException {
public BookIdMismatchException() {
super();
}
public BookIdMismatchException(final String message, final Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public BookIdMismatchException(final String message) {
super(message);
}
public BookIdMismatchException(final Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
这将使您了解这种全局异常处理机制的可能性。如果您想看到完整的实现,请看一看深入的教程:Error Handling for REST with Spring
注意,默认情况下,Spring Boot还提供了
/error映射。我们可以通过创建一个简单的error.html:
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>Error Occurred</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Error Occurred!</h1>
<div class="alert alert-danger" role="alert">
<b>
[<span th:text="${status}">status</span>]
<span th:text="${error}">error</span>
</b>
<p th:text="${message}">message</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
我们可以在 resources/application.properties 加入一个简单的属性来控制:
server.error.path=/error2
测试
最后,让我们测试一下我们的Book API。
我们可以使用 @SpringBootTest 加载应用程序的context 并验证运行应用程序时没有错误:
package com.onetree.starpath;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class StarpathApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
}
接下来,让我们添加一个JUnit测试,它使用RestAssured验证对我们编写的API的调用,
所以在 build.gradle 加一下 RestAssured的依赖:
// 一款简化test的Java的DSL
testImplementation 'io.rest-assured:rest-assured:4.2.0'
testImplementation 'io.rest-assured:json-path:4.2.0'
testImplementation 'io.rest-assured:xml-path:4.2.0'
然后 添加测试文件:test/java/{package}/BookTests.java
package com.onetree.starpath;
import static org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomStringUtils.randomAlphabetic;
import static org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomStringUtils.randomNumeric;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import com.onetree.starpath.persistence.model.Book;
import java.util.List;
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import io.restassured.response.Response;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
@SpringBootTest
public class BookTests {
private static final String API_ROOT = "http://localhost:8081/api/books";
@Test
public void whenGetAllBooks_thenOK() {
final Response response = RestAssured.get(API_ROOT);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.OK.value(), response.getStatusCode());
}
@Test
public void whenGetBooksByTitle_thenOK() {
final Book book = createRandomBook();
createBookAsUri(book);
final Response response = RestAssured.get(API_ROOT + "/title/" + book.getTitle());
assertEquals(HttpStatus.OK.value(), response.getStatusCode());
assertTrue(response.as(List.class)
.size() > 0);
}
@Test
public void whenGetCreatedBookById_thenOK() {
final Book book = createRandomBook();
final String location = createBookAsUri(book);
final Response response = RestAssured.get(location);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.OK.value(), response.getStatusCode());
assertEquals(book.getTitle(), response.jsonPath()
.get("title"));
}
@Test
public void whenGetNotExistBookById_thenNotFound() {
final Response response = RestAssured.get(API_ROOT + "/" + randomNumeric(4));
assertEquals(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value(), response.getStatusCode());
}
// POST
@Test
public void whenCreateNewBook_thenCreated() {
final Book book = createRandomBook();
final Response response = RestAssured.given()
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
.body(book)
.post(API_ROOT);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.CREATED.value(), response.getStatusCode());
}
@Test
public void whenInvalidBook_thenError() {
final Book book = createRandomBook();
book.setAuthor(null);
final Response response = RestAssured.given()
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
.body(book)
.post(API_ROOT);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), response.getStatusCode());
}
@Test
public void whenUpdateCreatedBook_thenUpdated() {
final Book book = createRandomBook();
final String location = createBookAsUri(book);
book.setId(Long.parseLong(location.split("api/books/")[1]));
book.setAuthor("newAuthor");
Response response = RestAssured.given()
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
.body(book)
.put(location);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.OK.value(), response.getStatusCode());
response = RestAssured.get(location);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.OK.value(), response.getStatusCode());
assertEquals("newAuthor", response.jsonPath()
.get("author"));
}
@Test
public void whenDeleteCreatedBook_thenOk() {
final Book book = createRandomBook();
final String location = createBookAsUri(book);
Response response = RestAssured.delete(location);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.OK.value(), response.getStatusCode());
response = RestAssured.get(location);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value(), response.getStatusCode());
}
// ===============================
private Book createRandomBook() {
final Book book = new Book();
book.setTitle(randomAlphabetic(10));
book.setAuthor(randomAlphabetic(15));
return book;
}
private String createBookAsUri(Book book) {
final Response response = RestAssured.given()
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
.body(book)
.post(API_ROOT);
return API_ROOT + "/" + response.jsonPath()
.get("id");
}
}

Comments